Duplicate content is a stealthy SEO killer. It silently tanks your traffic, confuses search engines, and leaves your site struggling for visibility. The result? A traffic ghost town, low on visitors and even lower on conversions.
But even though duplicate content can hurt you in the short term, this doesn’t have to be a rankings death sentence.
Resolving duplicate content issues can help reclaim lost rankings, drive more qualified traffic, and improve conversions.
I experienced this firsthand while working on an ecommerce project for a fashion retailer. By resolving duplicate content issues on just 10 product pages, I saw a significant impact—rankings improved for 200 keywords in just four months.
By consolidating duplicate URLs, rewriting product descriptions, and setting up proper redirects, we transformed a struggling website into a high-performing one.
And by the end of this article, I’ll teach you how to do the same. You’ll learn:
- What duplicate content is and how it impacts your SEO strategy.
- Common causes of duplicate content in ecommerce.
- Practical techniques to clean up and future-proof your website.
Ready to snatch your rankings back and make your traffic soar? Let’s dive in!
Not sure what’s holding your site back?
Our technical SEO services reveal hidden issues—and how to fix them—to improve your site’s performance.
What Is Duplicate Content in SEO?
In SEO, duplicate content refers to blocks of content—text, images, or metadata—that are identical or substantially similar and appear on multiple URLs within the same website or across different domains.
This duplication leaves search engines scratching their heads, unsure which version to rank for a search query.
Duplicate content won’t get you a Google penalty, but it will sabotage your SEO efforts, making it harder to achieve your business and content marketing goals.
Types of Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can be categorized into two primary types:
- Internal Duplicate Content: This occurs when identical content appears on multiple URLs within the same website. For instance, an ecommerce product page might repeat the same descriptions across the main category page, subcategory pages, and search results pages. This redundancy confuses search engines and irritates users who see the same thing over and over.
- External Duplicate Content: This happens when similar or identical content exists on different domains. A common scenario is when retailers copy product descriptions directly from a manufacturer’s website. This practice can lead to multiple websites competing against each other with carbon-copy content, reducing the likelihood of your site standing out and ranking well.
Duplicate Content in the Wild
Imagine you operate an online store selling fitness equipment. If your product description for “adjustable dumbbells” is copied verbatim from the manufacturer’s website or reused across multiple pages within your site, you create confusion for search engines.
Google (and others) may struggle to decide whether to rank your product page, the manufacturer’s page, or other competing pages with the same description. As a result, none of these pages may achieve optimal visibility.
Examples of Duplicate Content in Ecommerce
Duplicate content is a common challenge in ecommerce, often arising from the following scenarios:
- Product Descriptions: Many ecommerce stores copy product descriptions directly from manufacturers, producing identical content across numerous websites. This lack of originality hampers your ability to stand out in search results.
- Pagination Issues: Product listings that span multiple pages can inadvertently generate duplicate content if pagination is not correctly configured. For example, each paginated URL might include the same meta descriptions and titles.
- Filtered Results: Filtering products by attributes like size, color, or price often creates multiple URLs that display similar content. For instance, a filter for “blue sneakers” might generate a unique URL, but the core content remains unchanged.
These scenarios aren’t just annoying; they threaten to strip away all the benefits of ecommerce SEO you worked so hard to employ.
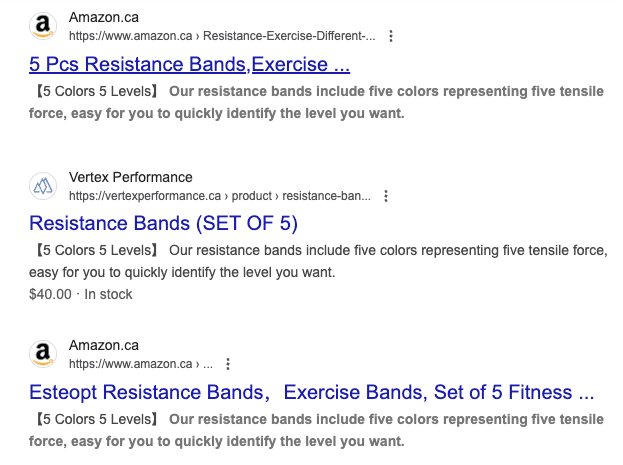
Multiple search results showcase the same resistance bands, all with identical descriptions across different sellers and platforms. This redundancy doesn’t just confuse search engines—it forces your listings to compete against each other, ultimately weakening your SEO efforts.
Why Understanding Duplicate Content Matters
Grasping the nuances of duplicate content is the first step to tackling it head-on. Identifying these challenges is the first step toward crafting a strategy to optimize your website and improve its SEO performance. In the next section, we’ll dive into how duplicate content impacts your SEO strategy and why addressing these issues is essential.
How Duplicate Content Impacts Your SEO Strategy
Duplicate content can be a sneaky saboteur for your SEO strategy. While it may not lead to direct penalties from search engines, it creates complications that hinder your site’s ability to rank competitively.
Understanding these impacts is crucial to fixing and preventing duplicate content issues on your ecommerce website. Here’s how it can hurt:
Reduced Organic Visibility
Duplicate content splits ranking potential across multiple URLs, making it harder for any one page to perform well in search results. Here’s what happens:
- Search Engine Confusion: Search engines like Google aim to provide users with the best possible results. When duplicate pages exist, search engines must prioritize one while sidelining others, even if those sidelined pages are valuable to users.
- Keyword Cannibalization: When multiple pages target the same keyword with identical or similar content, they compete against each other. This keyword cannibalization often results in all pages ranking lower than they otherwise would if consolidated.
For example, I once worked on an ecommerce site selling athletic shoes. They had multiple pages targeting “best running shoes” with similar content. Because of this, none of them ranked well. After consolidating these pages into a single authoritative page, we saw a 30% increase in traffic to that section alone.
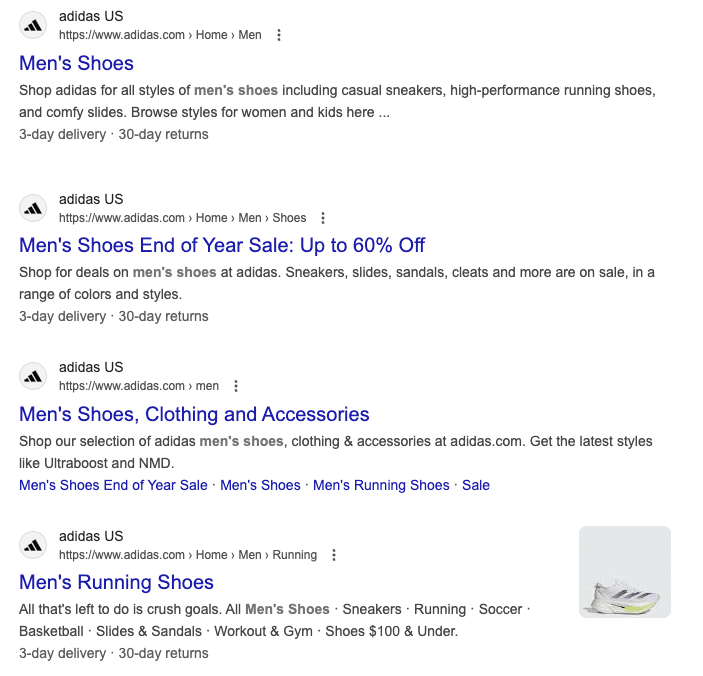
Duplicate content and keyword cannibalization can lead to multiple pages from the same site competing against one another in search results, as shown here. Instead of consolidating authority into a single high-ranking page, the visibility is diluted, reducing the overall SEO effectiveness.
Inefficient Indexing
Search engines use a finite crawl budget to index your site. Duplicate content consumes this budget unnecessarily, leaving less room for unique and updated pages to be indexed effectively. This can result in:
- Orphaned Pages: Valuable pages might remain unindexed because search engines are stuck crawling duplicate ones.
- Slower Updates: When duplicate pages are present, search engines may take longer to index new or updated content.
For ecommerce websites swimming in product pages, this means slower rankings for your latest launches, hurting both visibility and revenue.
Potential Risks to Your Site
Duplicate content doesn’t always come with an explicit penalty, but it introduces risks that can cripple your SEO and brand reputation. Here’s what’s at stake:
- Diluted Authority: Backlinks and topical authority that could boost one page are instead spread thin over duplicate pages, weakening their overall impact.
- Poor User Experience: Users navigating your site may encounter multiple pages with the same content, which can be confusing and frustrating and drive them away. This can increase bounce rates and reduce conversions.
- Third-Party Risks: If external websites steal or use your content without permission, search engines might attribute it to them instead of you. This hurts small brands even more, especially when competing against bigger names.
In one case, a client’s content was being copied by an unauthorized third-party site. Because their original content lacked proper canonicalization,
Google ranked the duplicate site higher. By reclaiming authority through proper canonical tags and a DMCA takedown, we restored their rankings within weeks.
Frequent Causes of Duplicate Content in Ecommerce
In ecommerce, duplicate content creeps up due to technical hiccups and rushed content creation strategies.
Understanding the root causes can help you identify and address these problems effectively. This section will break down the primary causes into three categories: technical setup challenges, content duplication practices, and external factors.
Technical Setup Challenges
The way your ecommerce site is set up might be creating duplicate URLs without you even realizing it.
Improper Use of Canonical URLs
Canonical tags are critical for guiding search engines to the primary version of a page. If you skip or botch their implementation, here’s what can happen:
- Multiple Indexed Versions: Search engines index multiple URLs for the same content, such as variations of a product page that feature tracking parameters or filters.
- Missed Consolidation Opportunities: Without proper canonical tags, link equity and authority are scattered between duplicate pages instead of consolidated into a single power page.
For example:
- example.com/product-page
- example.com/product-page?utm_source=newsletter
If no canonical tag is used to point to the primary version, both pages compete for rankings.
Tracking Parameters in URLs
Businesses often use tracking parameters in URLs for analytics and advertising. While useful for data collection, these parameters can create duplicate content headaches:
- example.com/shoes?source=google
- example.com/shoes?source=facebook
Both URLs point to the same product but are treated as separate pages by search engines. As a result, your ranking signals—and search engine love—get diluted.
Unoptimized Cart and Search Result Pages
Cart and search result pages are vital for user experience but add no SEO value. When indexing these pages, they clog up search engine results and squander your crawl budget.
- Cart Pages: These often contain unique-to-user, dynamic content that should not be indexed.
- Search Result Pages: Without proper configuration, search results can generate countless URLs like example.com/search?q=shoes, spawning duplication galore.
Inconsistent URL Structures
URL inconsistencies are a common technical flaw that creates duplicate content:
- Trailing Slashes: example.com/products vs. example.com/products/
- Uppercase vs. Lowercase: example.com/Shoes vs. example.com/shoes
- WWW vs. Non-WWW: www.example.com vs. example.com
Search engines treat each variation as a distinct URL unless proper redirects or canonical tags are in place.
Content Duplication Practices
Content duplication often stems from internal processes, particularly when scaling product listings is a priority.
Reused Product Descriptions
One of the most common causes of duplicate content is recycling manufacturer-provided product descriptions. While this saves time, it creates issues:
- Identical Content Across Sites: Competing ecommerce sites using the same descriptions create duplication across domains, making it a nightmare for any one site to rank well.
- No Unique Value: Search engines prioritize unique content that adds value. Reused descriptions fail to meet this standard.
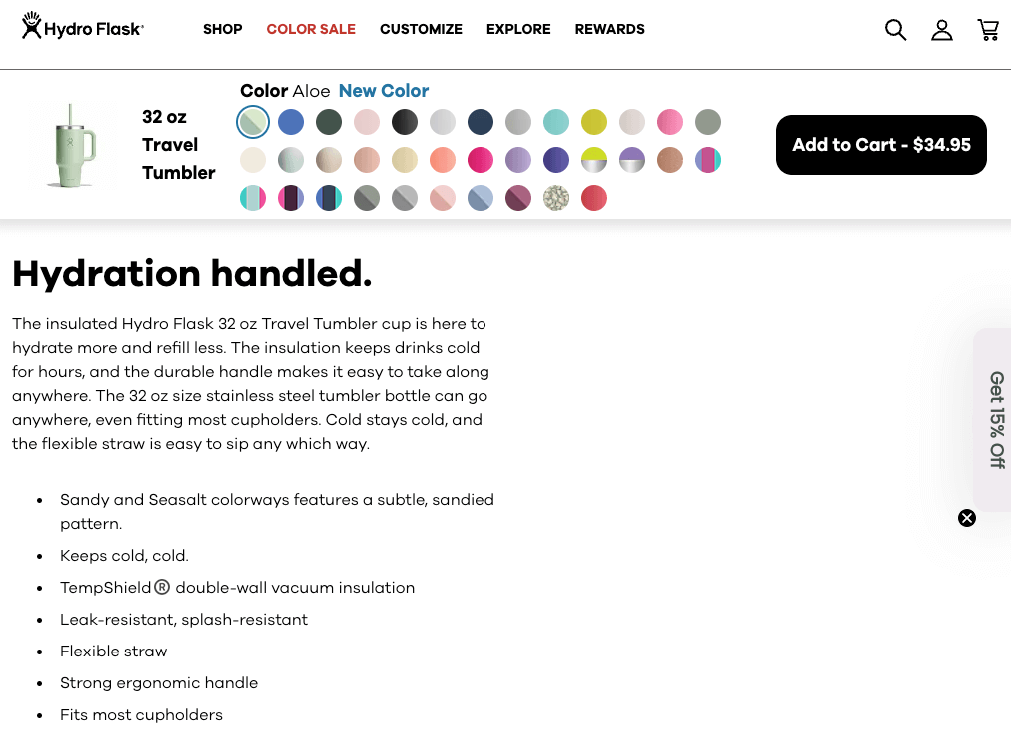
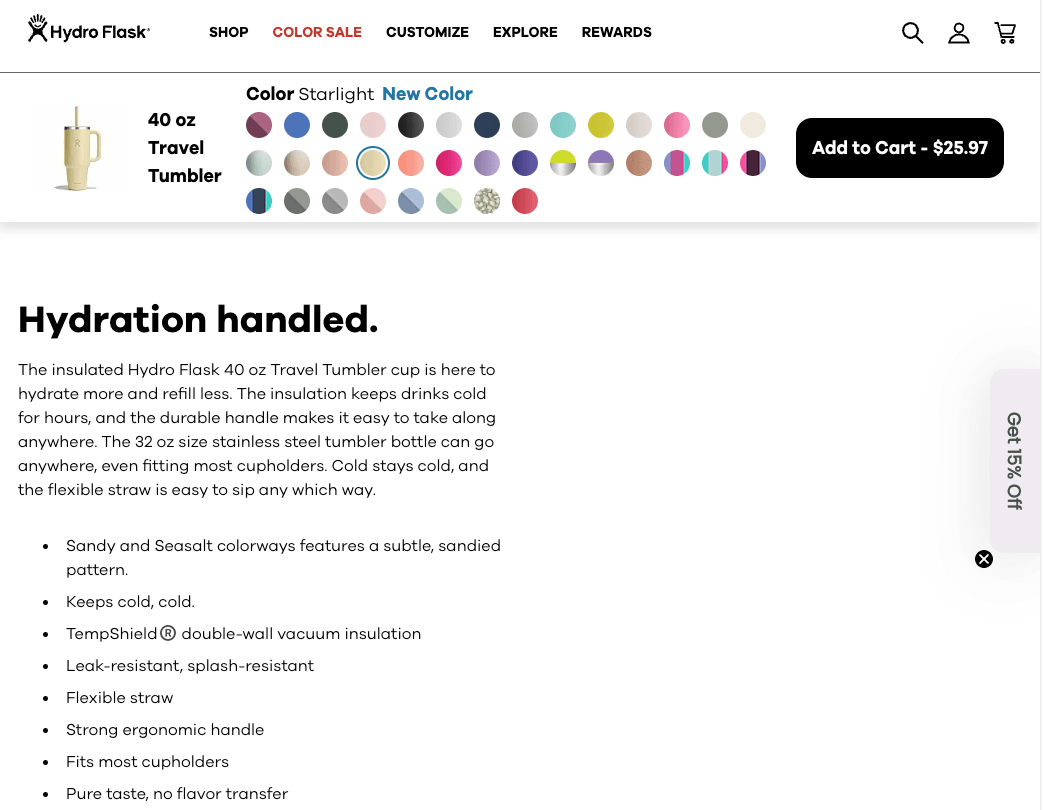
Both product pages display identical descriptions for different-size hydro flasks, offering no unique value to search engines. This duplication weakens SEO efforts and makes it harder for products to rank.
Creating unique, detailed descriptions for each item is key to standing out and improving search performance.
Generic Category Pages
Generic text on category pages, such as “Browse our wide selection of products,” adds no value and screams “generic!” to search engines. Without unique introductory text, these pages are SEO dead ends.
External Factors
Sometimes, duplicate content originates outside your control and can hurt just as much. These include:
Manufacturer Content
When retailers lean on manufacturer descriptions and specs, they all have identical content. This leads to identical product pages across multiple sites, leaving your site buried in the rankings shuffle.
Third-Party Platforms
Selling on third-party platforms like Amazon, eBay, or Shopify can create duplicate content issues when product listings are copied directly from your site. Worse, search engines might rank the third-party page higher than yours—even though it’s your content!
Scraped Content
Scrapers—those sneaky sites lifting your product descriptions or blog posts—can cause duplicate content headaches. Smaller ecommerce sites are especially vulnerable to this issue, as search engines might credit the copycat instead of you.
The Ripple Effect of Neglecting These Causes
Ignoring duplicate content doesn’t just impact SEO; it hurts your entire business.
You’ll lose rankings, dwindling traffic, missed sales, and a hit to your credibility. By tackling these root causes, you can improve visibility and user experience.
Best Practices to Avoid Duplicate Content
Preventing duplicate content is a proactive process that combines technical optimization, strategic content creation, and regular monitoring.
Follow these best practices to avoid the duplicate content trap and keep your ecommerce site optimized for search engines and users.
Use Redirects
Properly implemented redirects are your SEO safety net, ensuring your rankings stay strong.
Redirects are a fundamental tool for managing duplicate content issues effectively. They ensure both users and search engines are directed to the preferred page version, keeping the user journey smooth and your technical SEO intact.
When duplicate pages are identified or content needs to be consolidated, implementing a 301 redirect is a reliable solution that signals search engines which page to prioritize.
Redirects are particularly handy for cleaning up duplicate content messes: They can address outdated or redundant product pages, ensuring that users searching for these pages are directed to relevant alternatives. Also, suppose you merge multiple product listings into a comprehensive page. A 301 redirect ensures that all previous traffic and link equity are transferred to the new, consolidated version.
Fix pesky URL inconsistencies—think trailing slashes or www vs. non-www—with redirects to keep your site structure clear and authoritative.
For example, redirecting a URL such as example.com/product1 to a more structured and hierarchical URL such as example.com/product-category1/product1 not only resolves duplication but also enhances the clarity of your site’s structure.
One of our ecommerce clients had multiple URLs for the same product due to tracking parameters. By implementing 301 redirects, we boosted their product page ranking by 25% within three months
This practice consolidates link equity, directing SEO value to the appropriate page and ensuring your content hierarchy is clear to users and search engines.
Regularly Audit Your Site
Regular audits are essential to identify and fix duplicate content issues before they chip away at your rankings. That’s why it’s one of the key ecommerce SEO services we offer our clients.
There are multiple tools you can use to do this:
- Screaming Frog: Crawls your site to detect duplicate pages, meta tags, and canonicals.
- Google Search Console: Identifies indexing issues and highlights potential duplication.
- Copyscape or Ahrefs: Detects external duplication, such as scraped content.
Focus your audits on key areas, including product pages with reused descriptions, category pages with generic or repeated text, and URLs with parameter or structural inconsistencies.
Routine checks ensure your site stays clean, optimized, and ready to rank.
Optimize with Canonical Tags
Canonical tags are your ally in guiding search engines to the preferred version of a page. They’re especially useful for product pages that have variations or dynamic filters.
By assigning a canonical tag to each page’s primary version, you tell search engines exactly which version to index and rank.
Example: For product variations like:
- example.com/shoes?color=red
- example.com/shoes?color=blue
Set the canonical tag for both to:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/shoes" />
This ensures search engines only index the primary URL, preserving the strength and authority of your preferred page.
Combine Similar Pages
Do you have pages that overlap or target the same keyword? Stop letting them cannibalize each other and merge them into one supercharged page.
Combining similar pages into a comprehensive resource boosts rankings, consolidates link equity, and creates a go-to resource for your audience. For example:
- Merge “Running Shoes for Beginners” and “Best Running Shoes for New Runners” into one targeted page.
- Consolidate seasonal or time-sensitive content into evergreen guides that deliver lasting value.
By doing this, you will simplify your site, rank higher, and better serve users and search engines.
Block Non-Essential Pages
Not every page on your site deserves to be indexed by search engines. Blocking non-essential pages lets you focus your site’s crawl budget on the content that truly matters.
Pages to Block
- Cart and Checkout Pages: These are important for users but offer no SEO value. Indexing them just muddies the search engine waters.
- Login or User Account Pages: Login portals and user profiles are not in search results. Block them to keep them off Google’s radar.
- Search Results Pages: Product filter results or internal search pages create duplicate content that doesn’t help SEO.
How to Block Effectively
Using robots.txt
The robots.txt file is a powerful tool for instructing search engines to avoid crawling certain pages. It’s an efficient way to block large sections of your site that don’t need to be indexed.
Example robots.txt Directive:
User-agent: * Disallow: /cart/ Disallow: /search/
In this example, search engines are instructed not to crawl URLs containing /cart/ or /search/, effectively excluding these pages from indexing.
Applying Noindex Meta Tags
For more precise control, you can add a noindex meta tag to the HTML of specific pages. This tag tells search engines not to index the page, even if they discover it.
Example Noindex Tag:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">
This tag can be placed in the <head> section of pages like login portals, user profiles, or any other private or redundant content.
Prioritize Unique Content Creation
Nothing beats original, high-quality content. If you want to stand out, don’t cut corners—ditch the manufacturer’s descriptions and focus on creating unique, engaging product pages.
Tips for Unique Product Content
- Rewrite product descriptions in your brand’s voice. Highlight features, benefits, and what makes each product special.
- To make your product pages richer than your competitors’, include extra value like customer reviews, FAQs, or usage tips.
Don’t ignore category pages! Adding punchy, SEO-optimized intros makes them compelling for both users and search engines.
By investing in original content, you’ll earn trust, engage customers, and lock in higher rankings.
Noindex WordPress Tag or Category Pages
For WordPress/Woocommerce stores:
Tags and category pages often duplicate content from product pages, adding no SEO value and cluttering search results. Instead of letting these pages weaken your SEO, apply a noindex directive.
Use tools like Yoast SEO to easily set tag and category pages to noindex. This keeps search engines focused on your highest-value content.
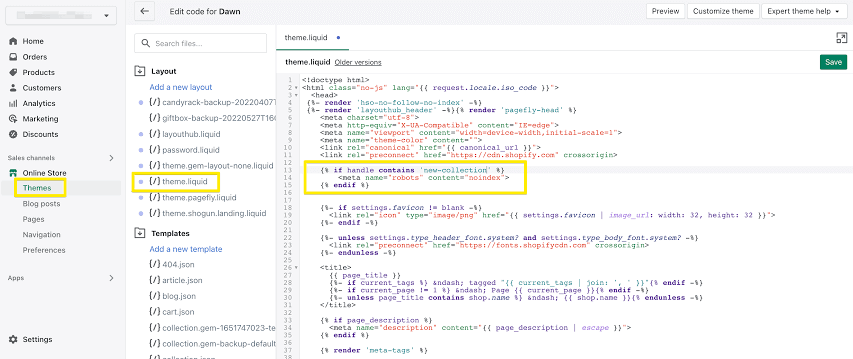
For Shopify stores:
The highlighted code shows how to modify the theme.liquid file to include a noindex tag. This ensures that search engines prioritize your high-value content and keep your Shopify store’s SEO strategy on track.
If your store is running on Shopify, I recommend you read my article: Shopify Ecommerce SEO Checklist: Rank Higher and Sell More!
A Workflow for Implementing These Practices
Streamline the process of fixing and preventing duplicate content with this four-step workflow:
- Audit Your Site: Use tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console to identify duplicate content, inconsistent URLs, and poorly performing pages.
- Prioritize Fixes: Start with high-priority pages, like key product listings or category pages. Fix canonical tags, apply redirects, and remove non-essential pages from indexing.
- Create Unique Content: Rewrite product descriptions and category intros, add multimedia elements, and emphasize freshness. Refreshing old content is also worth pursuing.
- Set Up Monitoring: Use automated tools to track your progress and catch duplicate content issues before they snowball.
Don’t Let Duplicate Content Detail Your Ecommerce Efforts
Duplicate content might be lurking in your ecommerce site, silently wrecking your SEO efforts. But with the right tools and strategies in place, you can fix it—and keep it from coming back.
By implementing these best practices, you’ll transform your site into an SEO powerhouse that ranks higher, draws more traffic, and converts like never before.
Not to brag (okay, maybe a little), but we have a lot of experience dealing with duplicate content and any other SEO issues that might be plaguing your site.
If you want to eliminate the guesswork and work with an experienced team that can get your site to the top of the rankings, contact us today.

