Whether you’re in the business of fashion ecommerce, selling travel suitcases, or peddling camera lenses, getting your customers’ eyeballs on your product should be at the top of your list of priorities.
One of the most effective ways to capture that attention is through well-optimized category pages, also known as Product Listing Pages (PLPs).
Think of these pages as the digital aisles of your online store. They guide potential customers to the products they’re looking for.
However, if you don’t optimize these pages correctly, you’ll miss out on significant traffic and sales opportunities.
To plug this hole, I’ll show you how to optimize your ecommerce category pages for SEO so they’re both discoverable and user-friendly.
Let’s jump in!
Originally published on August 27, 2024, this article was republished on March 20th, 2025.
Has Your Store Lost Key Rankings?
We’ve conquered some of the most competitive D2C markets in the world – from women’s fashion to adult toys, subscription boxes to golf apparel.
If your business deserves to be on top, we’ll get you there.
How Ecommerce Category Pages Help Your SEO
PLPs are critical components of an ecommerce website’s structure. They are the main traffic-generating pages for ecommerce sites, often ranking for high-volume terms that help potential customers discover your brand.
While a page for a specific product can rank well, PLPs will typically rank for higher volume terms.
For example, while a well-optimized Product Description Page (PDP) might rank for a type of jeans, a PLP could rank for the broader and more competitive term “Men’s Jeans.”
On top of that, PLPs are essential for SEO because they:
Drive More Organic Traffic
PLPs can be a powerhouse for organic traffic, especially when optimized for long-tail keywords. These keywords often align with high-intent, transactional queries, meaning users searching for them are already considering a purchase.
When properly structured, PLPs can bring in a significant percentage of organic traffic. For example, we recently optimized category pages for a client and saw their organic traffic skyrocket, outperforming even some individual product pages.
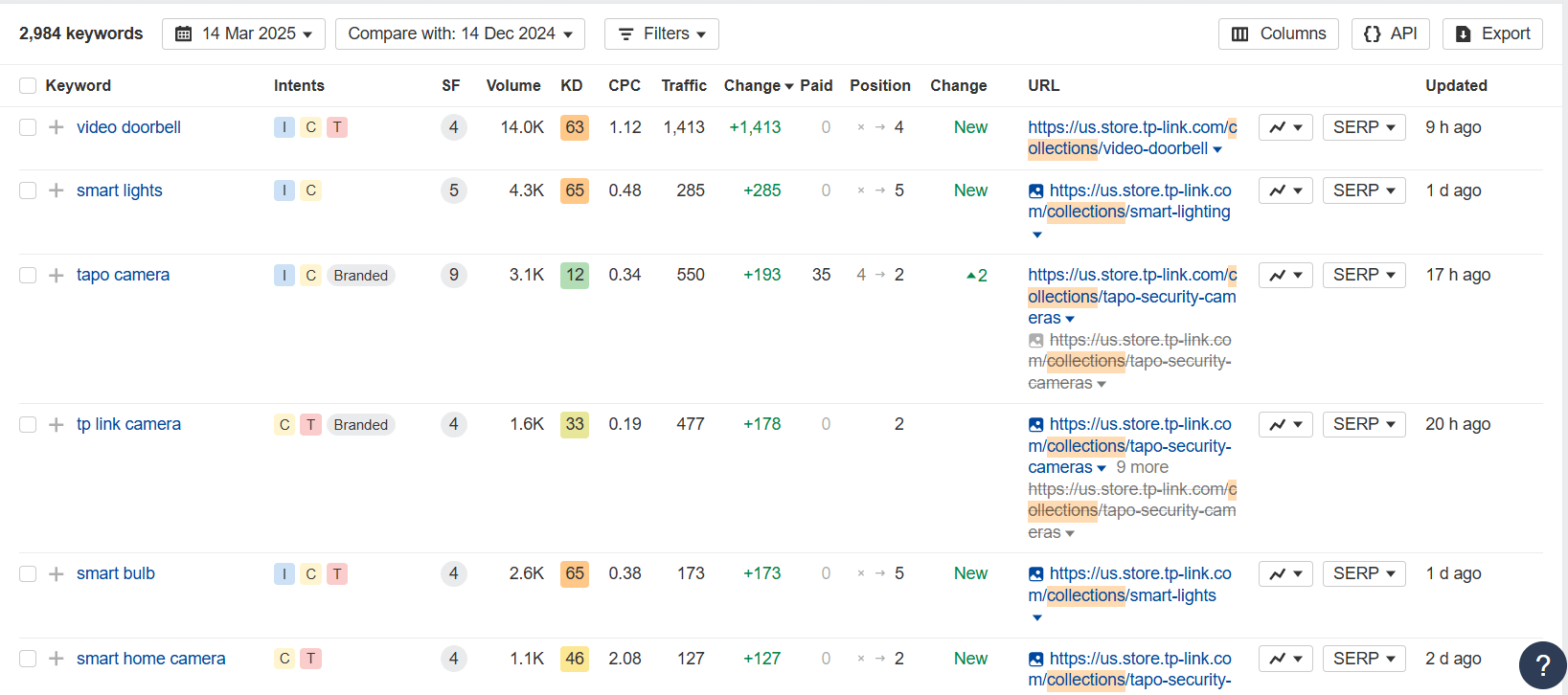
This happens because PLPs naturally capture a broad range of search terms by including variations in product attributes, such as size, color, and brand.
A well-optimized PLP can rank for dozens—sometimes even hundreds—of related searches, making it a critical component of your SEO strategy.
Boost Brand Visibility and Drive More Clicks
Brand visibility in search results means that when users look for products in your niche, your site consistently appears in the search listings. But visibility alone isn’t enough – it has to be strategic.
For example, imagine someone searches for “best business casual shirt” and lands on a well-optimized PLP from your store rather than a competitor’s. In that case, they’re introduced to your brand even if they weren’t specifically searching for it. Over time, this repeated exposure builds recognition, trust, and ultimately, customer loyalty.
Improve Conversions by Simplifying Navigation
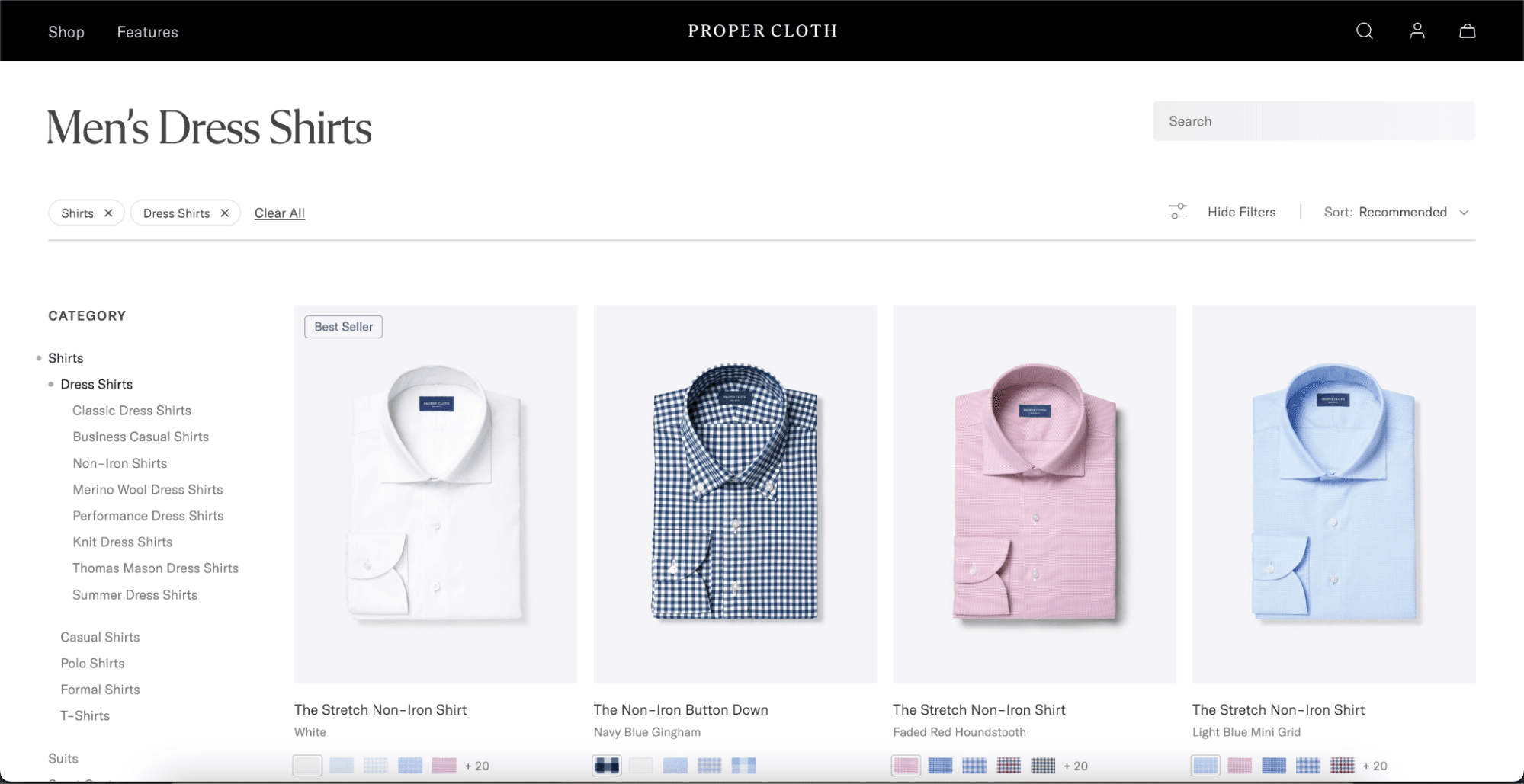
PLPs are crucial in the conversion funnel. They guide users from product discovery to purchase with minimal friction.
Think about it this way:
- A visitor lands on a broad category page (e.g., “Men’s Dress Shirts”).
- They use filters to narrow options by size, price, or brand.
- They find a product that matches their criteria and click through to purchase.
The fewer steps a person takes to find what they need, the higher the likelihood of conversion. Every additional click or unnecessary step introduces friction and can lead to drop-offs.
Strengthen Internal Linking for SEO and UX
Internal linking is essential for both search engines and users. It helps search engines understand site hierarchy and effectively distributes link equity. This ensures that important pages are correctly indexed and ranked.
Strong internal linking improves:
- Crawlability: Google bots can navigate and index your site more efficiently.
- Context: Links provide additional context for search engines about the relevance of a page.
- Authority Flow: Pages linked frequently gain more SEO value.
For example, linking from high-authority category pages to individual product pages helps distribute SEO value, improving rankings across the board.
On top of that, breadcrumb navigation on PLPs further strengthens internal linking while enhancing user experience.
Create Value with Unique Content on PLPs
Adding unique, valuable content to PLPs does more than just improve SEO—it enhances the user experience by answering key questions before a user even considers leaving the page.
Some of the best-performing PLPs include:
- Descriptive category text explaining the benefits of the products listed.
- FAQs addressing common concerns (e.g., “Is it easy to install Tapo cameras?”).
- Customer reviews providing real-world insights into product performance.

By leveraging these strategies, PLPs become more than just product directories—they become high-performing SEO assets that drive traffic, conversions, and brand recognition.
Ecommerce Category Pages SEO Best Practices
Now that you know why PLPs are essential for your ecommerce business’ success, how can you make these category pages more discoverable?
Here are a few best practices you can use to optimize your ecommerce category pages effectively:
1. Conduct Keyword Research to Expand the Number of PLPs/Categories/Collections
The first step to optimizing your category pages is conducting thorough keyword research. Whether you’re using Shopify or WooCommerce, understanding your customers’ search intent will help you better structure your PLPs.
Many businesses create PLPs based on their product catalog without considering search intent. By identifying competitor gaps, product attributes, and PDP intent, you can expand your PLP collection to cover your entire catalog while aligning with search intent and volume.
Targeting long-tail keywords allows you to match user intent more specifically and compete for less competitive terms.
For example, a PLP targeting “eco-friendly women’s shoes” is more likely to attract a niche audience ready to purchase than a generic “women’s shoes” category.
You can do this yourself using free or paid-for online tools, but you’re likely to get better results if you hire an external company with the expertise to identify the best keywords for your particular business. It’s part and parcel of ecommerce product SEO that will help the customers you want to find your products.
2. Organize Categories Hierarchically
Organizing your categories logically and hierarchically is essential for SEO and user experience. A well-structured site makes it easier for search engines to understand content relationships while helping users navigate efficiently.
One effective way to achieve this is by utilizing content hubs to build a strong site architecture.
While there are many different ways to structure and organize content, one that’s particularly useful for ecommerce businesses is the silo structure. It involves grouping related pages under broad categories, making it easier for search engines to understand your site’s URL structure.
Each silo consists of a main silo page and related content, all of which are interlinked. However, and this is a crucial point, the content in one silo does not link to the content in another silo.
For example, if you’re selling men’s wear, “Pants” might be the silo page, and linking and interlinking to that page would be “Jeans,” “Chinos,” and “Dress pants.”
Another silo might be “Shirts,” but because pants and shirts are distinct categories, the subpages in each silo would only link to their relevant parent pages and not across categories.

3. Add Useful Content
A successful PLP isn’t just a collection of product thumbnails. It should provide valuable information that guides the user through their buying journey.
Each of your category pages could benefit from the following:
- Descriptive Text: Include a brief overview of what the category offers, highlighting key benefits and features.
- FAQs: Address common questions and concerns related to the products in the category.
For instance, TP-Link’s category pages include detailed content that enhances users’ understanding of their product offerings.
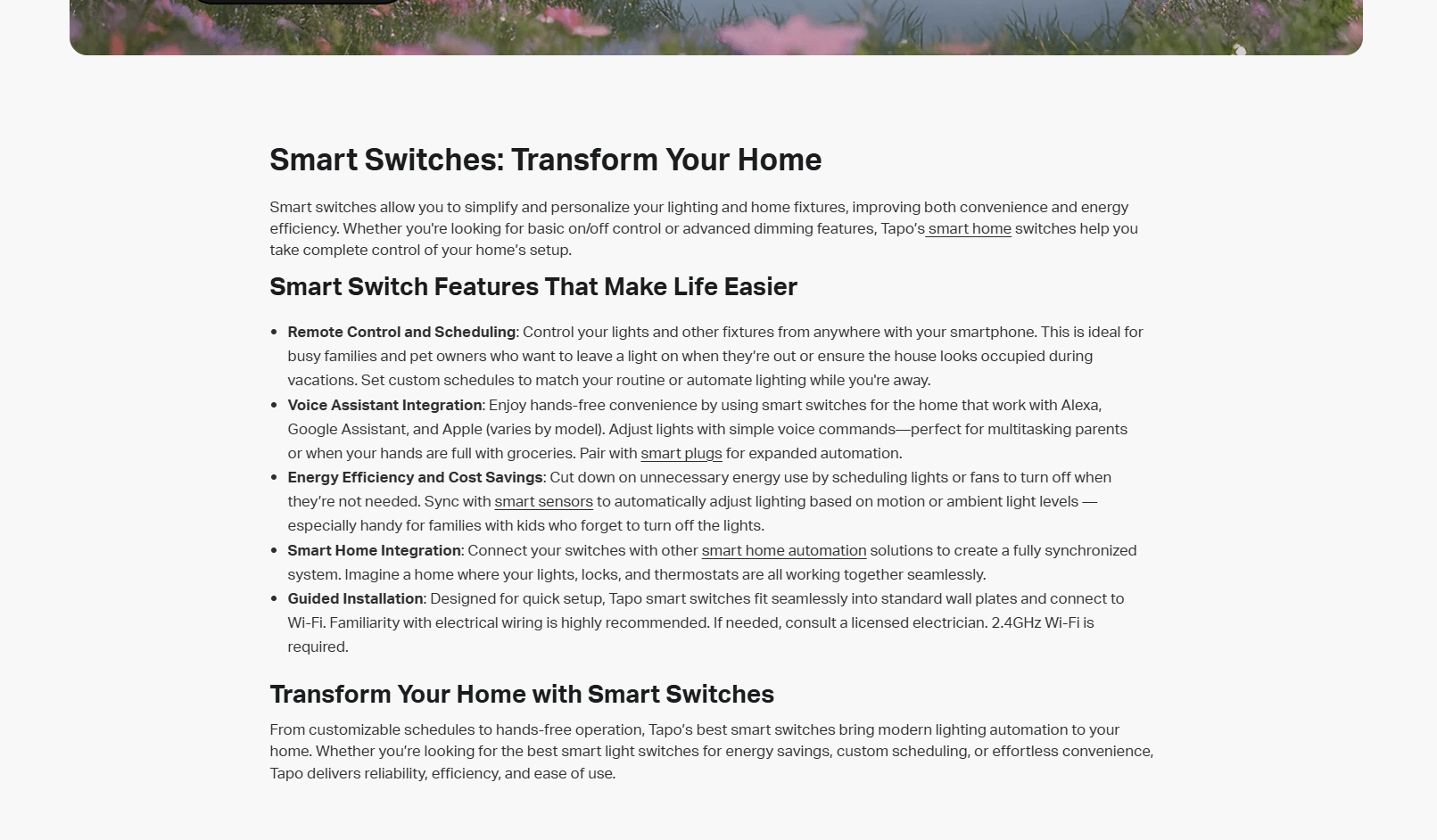
4. Have Proper Navigation
Proper navigation is critical for guiding users through your site and ensuring they can find what they need quickly.
Here are some elements of effective navigation:
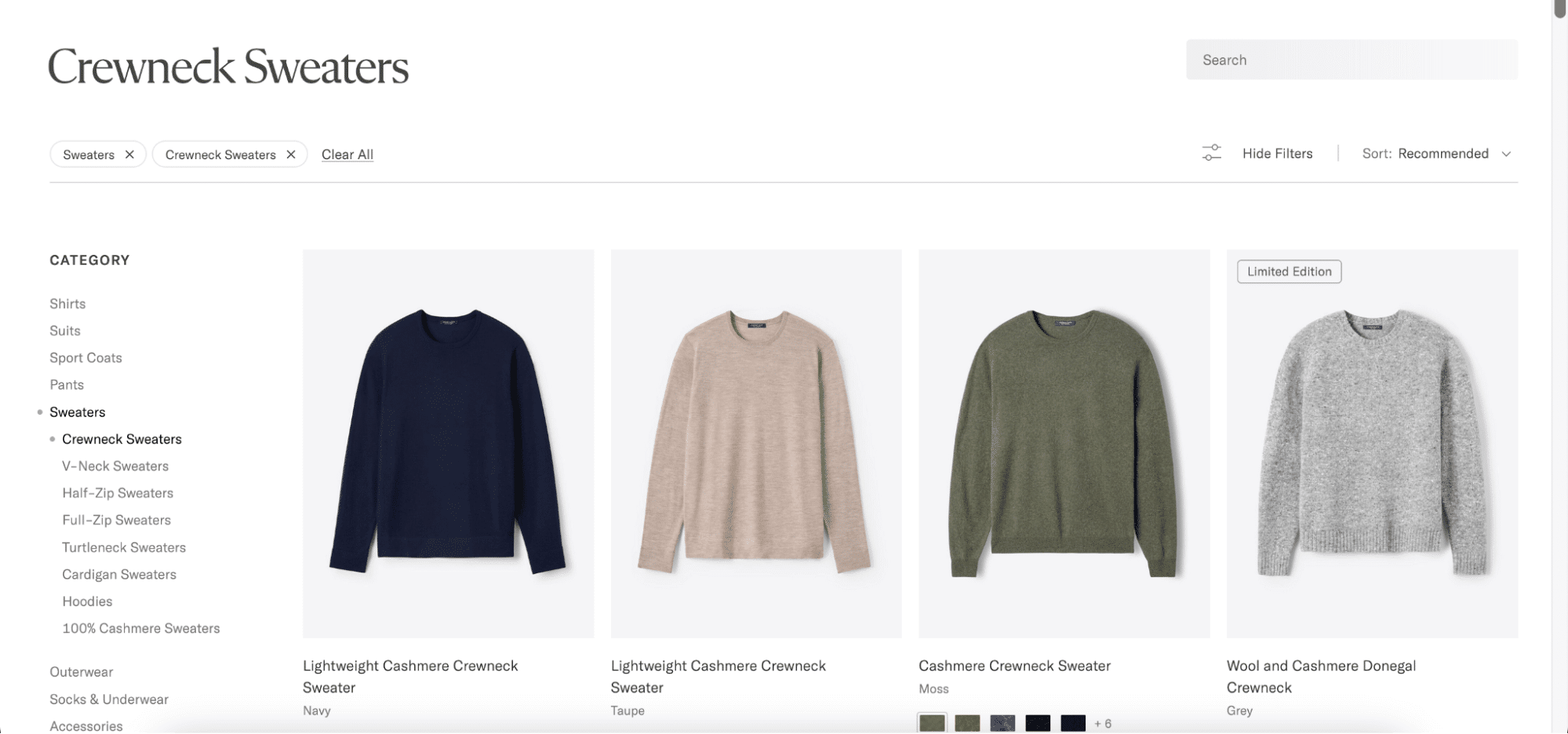
- Breadcrumbs: Breadcrumbs help users understand their location within the site hierarchy and easily navigate to previous pages. For example: “Sweaters” > “Crewneck Sweaters.”
- Navigation Menus: Clear and concise menus enable users to quickly find relevant categories and products
- Relevant Category Recommendations: Suggest related categories to keep users engaged and encourage further exploration. For example, if a user is browsing “Sweaters,” recommendations might include “Jeans” and “Belts” to promote further discovery.
- Internal Links: Use internal links to connect related content and guide users toward conversion paths. For example, a PLP relating to “Sweaters” might include internal links to related articles on “V-Neck Sweaters” and “Hoodies.”
5. Follow Best UX Practices for Usability
Usability is a critical factor in the success of ecommerce websites. It ensures that users can navigate the site easily, find what they’re looking for, and complete their purchase with as little frustration as possible.
According to Baymard’s extensive research on homepage and category navigation UX, several best practices can significantly enhance the user experience on category pages:
- Intuitive Design: Use a clean, simple design that prioritizes essential elements and minimizes distractions. By prioritizing key elements such as product listings and navigation options while at the same time reducing distractions such as banner ads, you can make it much easier for users to navigate your site and find the product they’re looking for.
- Consistent Layout: Maintain consistency in layout and design elements across all category pages, including filters and sorting options. This will help users become more familiar with your site and allow them to understand the navigation intuitively.
- Easy Filtering and Sorting: Provide users with options to filter and sort products based on their preferences. This includes attributes like size, color, and price and sorting options like popularity, price, or newest.
6. Ensure Your Design Is Accessible
Accessibility isn’t just a legal requirement for many sites; it’s also a crucial aspect of user experience. But what does accessibility mean from an ecommerce perspective?
Simply put, it’s ensuring that your site is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities such as low vision or blindness, hearing difficulties, or limited mobility.
Luckily, you don’t have to guess how to make your site more accessible.
Just follow the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) by incorporating features such as:
- Alt Texts: Use descriptive alt texts for images to assist visually impaired users.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure that all interactive elements can be navigated using a keyboard.
- Contrast and Readability: Use high-contrast colors and legible fonts to enhance readability for all users.
7. Link to Internal Useful Guides and Tools
Linking to internal guides and tools from a product page enhances user experience, provides valuable information, and improves SEO. Proper Cloth, for example, links to its Tuxedo Shirt Guide from its formalwear category page, offering users additional insights and increasing the time spent on the site.

Here’s how it helps:
- Provides Context: When users browse a site, they’ll likely have questions about using a certain product. Linking to a guide from a product page puts the relevant information directly in their laps without the user searching elsewhere. This makes the whole browsing experience that much more seamless. It also reduces friction by providing the user with detailed information about questions they might have about the product specifics.
- Educates Users: Since guides contain in-depth information about a specific product, they can help users feel more confident about their purchase. Imagine you’re buying a tuxedo shirt and are unfamiliar with the differences between pleated and pique fronts. Proper Cloth’s guide clarifies these options, helping you select the best product for your needs.
- Builds Trust and Authority: A detailed guide can position you as an expert in your field. Proper Cloth’s detailed guides demonstrate that they know more than a thing or two about formalwear, which can increase customer trust and loyalty. Shoppers appreciate brands that provide more than just products—they value those that help them make informed choices.
- Improved SEO: Linking internally to helpful content, such as guides, strengthens your site’s internal linking structure. It also increases the time users spend on your site, signaling to search engines that the content is valuable and boosting the site’s ranking. Finally, it allows you to target specific, long-tail keywords. For example, Proper Cloth’s guide might rank for search terms like “how to choose a tuxedo shirt” or “best tuxedo shirt for black-tie events.” This brings additional traffic to the site from people looking for detailed advice, not just products.
8. Follow Best On-Page Practices
On-page SEO optimization is one of the most important things you can do for your ecommerce category page. It improves the visibility and relevance of your ecommerce website and enhances its usability.
When optimizing the on-page on your site, here are a few things to consider:
- Unique and Targeted Titles: Title tags are crucial for SEO as they signal to search engines and users what the page is about. Craft unique and targeted titles that include primary keywords relevant to each page. Keep them concise (50-60 characters) and ensure they reflect the content accurately to improve click-through rates.
- Clean and Informative H1: The H1 tag is essential for communicating the page’s main topic to users and search engines. Use a single, well-optimized H1 tag that includes your target keywords. Ensure the H1 is descriptive and aligns with user search intent (e.g., product names or categories).
- Optimized Meta Descriptions: While meta descriptions don’t directly impact rankings, they influence click-through rates by summarizing the page. Write compelling meta descriptions (150-160 characters) that accurately describe the page content and include primary keywords. Highlight unique selling points and encourage users to click.
- SEO-Friendly URLs: Clean, readable URLs help users and search engines understand the page’s content. Keep URLs short, descriptive, and keyword-rich. Avoid complex structures with unnecessary parameters.
- Schema Markup: Adding schema markup can enhance your product listings in search results, leading to rich snippets that attract more clicks. Use product, review, and pricing schema to provide search engines with structured data, enhancing your listings’ visibility.
9. Optimize URL Structure for Better SEO and Navigation
Your URL structure plays a crucial role in both SEO and user experience. A well-organized, clean URL helps search engines understand your site hierarchy and makes it easier for users to navigate your store.
A messy, unstructured URL can confuse search engines and hurt rankings, while a logical, keyword-rich URL can improve visibility and click-through rates. Here’s how to optimize your structure:
Keep URLs Clean and Readable
A clean URL is short, descriptive, and free of unnecessary parameters. Instead of using complex URLs with random numbers and symbols:
propercloth.com/shop/item123?=p=5678&ref=xyz
Use a clear, structured format like:
propercloth.com/shop/shirts/dress-shirts
This makes it easy for users to understand where they are on your site and improves search engine indexing.
Follow a Logical Hierarchy
Your URL structure should mirror your site architecture, moving from broad categories to more specific pages. A well-structured ecommerce URL should look like this:
- propercloth.com/shop/(Main store page)
- propercloth.com/shop/shirts/(Category page)
- propercloth.com/shop/shirts/dress-shirts/(Subcategory page)
This approach reinforces topical relevance and strengthens internal linking, making it easier for search engines to crawl and rank your pages.
Use Keywords Naturally in URLs
Including keywords in your URLs can boost rankings, but they should be used naturally and sparingly. Instead of:
propercloth.com/shop/cat25/
Use:
propercloth.com/shop/shirts/dress-shirts/
This makes your URLs more relevant and readable for users and search engines.
Maintain Consistency and Best Practices
To avoid confusion and technical issues, stick to consistent URL formatting across your site:
- Use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) or spaces for better readability.
- Keep URLs lowercase to prevent duplicate content issues.
- Avoid deep nesting, which makes URLs unnecessarily long and harder to crawl.
10. Incorporate User Reviews and Ratings
User reviews and ratings are crucial in building trust, improving conversions, and enhancing SEO. When potential customers see real feedback from others, they feel more confident about their purchase decisions. Reviews act as social proof, reducing hesitation and increasing conversions.
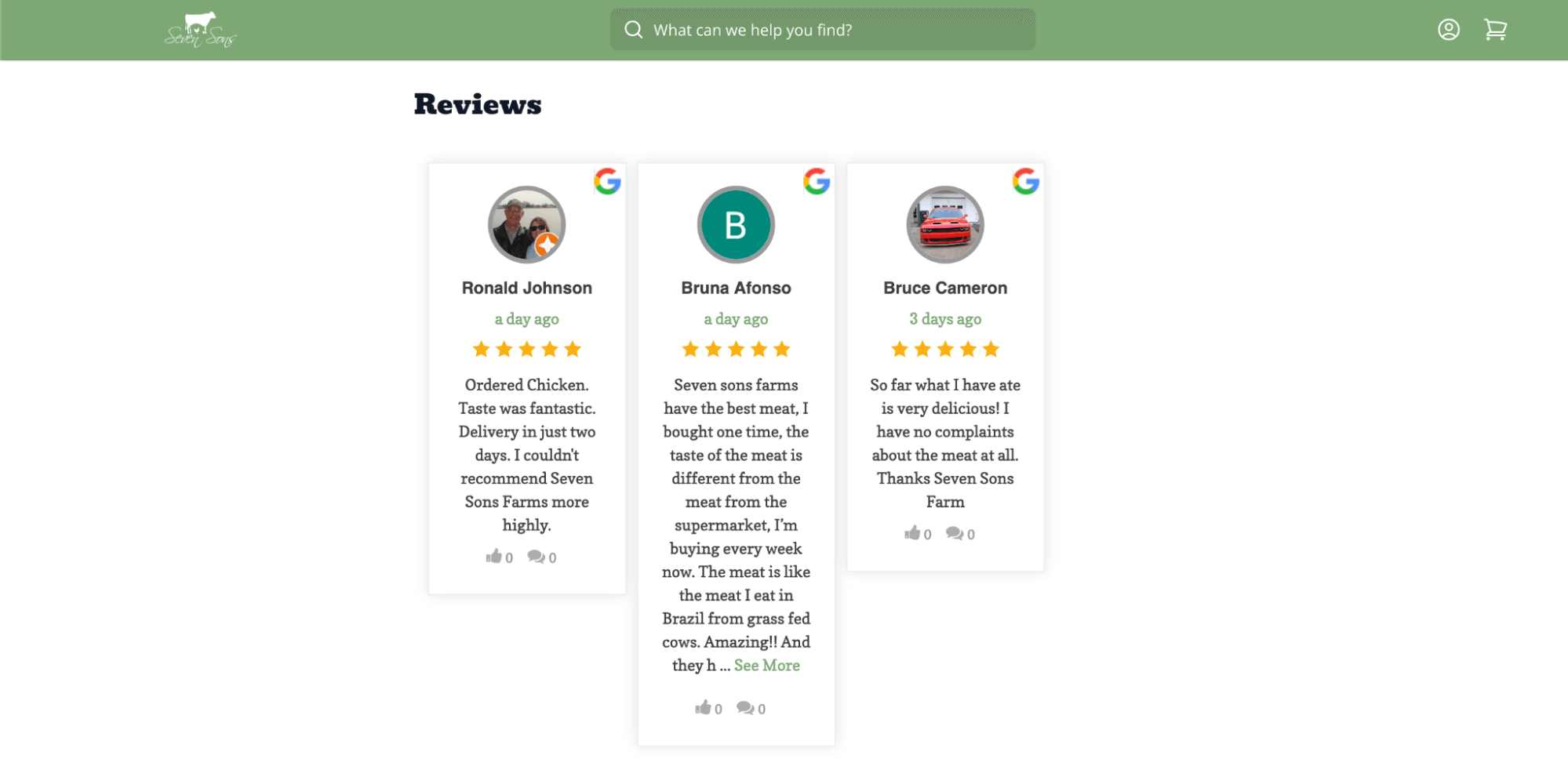
From an SEO perspective, reviews can enhance search visibility by adding fresh, user-generated content to your PLPs. Google often displays star ratings in search results, making your listings stand out and increasing click-through rates.
Reviews can:
- Boost Trust and Credibility: Genuine customer feedback increases confidence.
- Improve Search Appearance: Star ratings in rich results attract more clicks.
- Increase Conversions: People are most likely to trust products with reviews, leading to more conversions.
11. Utilize Structured Data Markup
Structured data markup is essential if you want your product listings to grab attention in search results.
Also known as ecommerce schema, structured data helps search engines understand the content on your pages and display rich results, such as star ratings, pricing, stock availability, and even shipping details. This makes your listings more visually appealing and informative, increasing your chances of getting clicks.
Implementing the right schema will help Google, AI-powered search assistants, and potential customers find and understand your products faster.
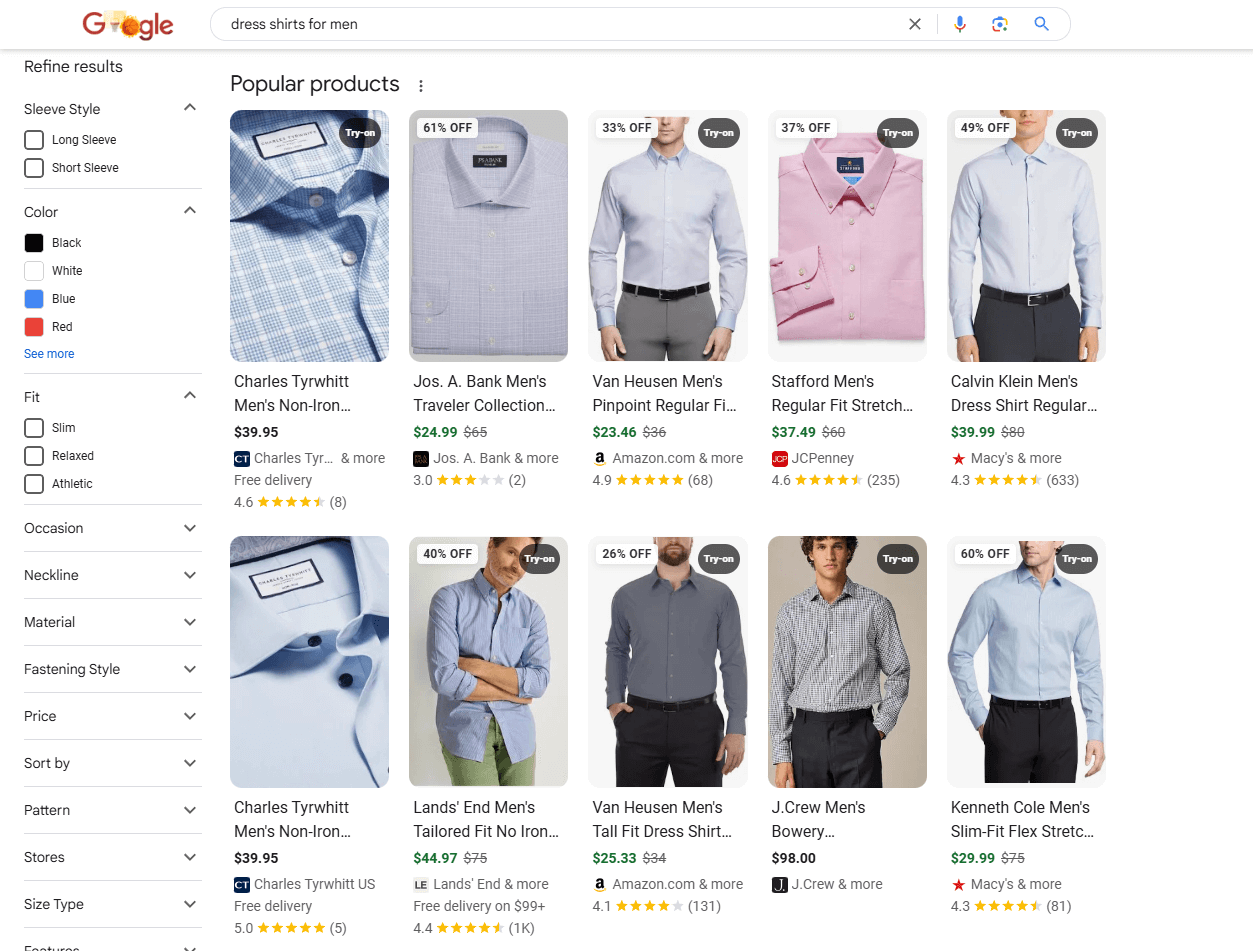
Many ecommerce platforms and SEO plugins offer built-in schema support, or you can manually add markup following Google’s guidelines.
After implementing it, test your schema with Google’s Rich Results Test to ensure everything works correctly.
Adding structured data might seem technical, but it’s one of the easiest ways to improve your store’s visibility, attract more clicks, and build trust with shoppers before they even land on your site.
12. Improve Page Load Speed
With most searches done on mobile devices, page speed is critical for SEO and user experience. Slow-loading pages cause frustration, increase bounce rates, and hurt conversions.
There are a few different ways to improve page load speed:
- Optimize Images: Use next-gen formats like WebP instead of JPEGs and PNGs.
- Enable Lazy Loading: Load images only when they come into view, reducing initial load time.
- Use a Fast Hosting Provider: Choose a CDN-backed hosting service for global speed improvements.
- Minimize JavaScript and CSS: Compress and defer non-essential scripts to speed up rendering.
Implementing these optimizations creates a seamless shopping experience, especially for mobile users who demand instant product access.
FAQs
What makes a good category page?
A good category page should be well-structured, user-friendly, and SEO-optimized. It should include a clear title, a concise description, and intuitive navigation to help users find products quickly.
It should also feature strong internal linking, relevant filters and sorting options, and optimized images for usability. Adding unique content like FAQs, buyer’s guides, and user reviews enhances SEO while helping customers make informed decisions.
What’s the difference between optimizing category pages and product pages?
Category pages target broader keywords and serve as a gateway to multiple products, while product pages focus on specific items with detailed descriptions, pricing, and specs.
Optimizing category pages involves improving navigation, internal linking, and structured data, whereas product pages require detailed content, high-quality images, and conversion-focused elements like reviews and CTAs.
Both play a key role in driving traffic and sales.
How much content should be added to a category page?
Category pages should have enough content to help search engines understand the page’s relevance without overwhelming users.
An introduction of 150–300 words explaining the category’s purpose, key product types, and benefits is ideal.
Adding FAQs, buyer’s guides, and short product descriptions provides value while keeping the page scannable.
Avoid excessive text above products—place longer content below listings to maintain a smooth shopping experience.
Is duplicate content a problem for category pages?
Yes, duplicate content can affect SEO, especially if multiple category pages feature the same descriptions or auto-generated filters create near-identical pages.
To prevent this, use unique category descriptions and canonical tags for similar pages and ensure filtered results don’t create duplicate URLs.
Implementing structured data and adding user-generated content (like reviews) helps differentiate your pages and improve rankings.
Category Pages Will Get You Sales. Let Us Optimize Them For You.
Optimizing ecommerce category pages for SEO is a multifaceted process that involves strategic planning, content creation, and technical optimization.
Following the tips outlined in this article can enhance your PLPs’ performance, improve user experience, and ultimately drive more traffic and sales to your site.
If you want to take your ecommerce SEO strategy to the next level, the team at DCP is here to help.
We specialize in tailored content marketing solutions that unlock your business’s full potential.
Check out our Ecommerce SEO Services page to learn more.

